Training Course on Vector Databases and Embeddings for Semantic Search
Training Course on Vector Databases & Embeddings for Semantic Search: Optimizing Similarity Search for LLM Applications provides a comprehensive deep dive into Vector Databases and Embeddings, equipping participants with the essential skills to revolutionize Semantic Search and optimize Large Language Model (LLM) applications.
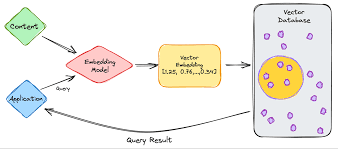
Course Overview
Training Course on Vector Databases & Embeddings for Semantic Search: Optimizing Similarity Search for LLM Applications
Introduction
Training Course on Vector Databases & Embeddings for Semantic Search: Optimizing Similarity Search for LLM Applications provides a comprehensive deep dive into Vector Databases and Embeddings, equipping participants with the essential skills to revolutionize Semantic Search and optimize Large Language Model (LLM) applications. In today's data-driven world, traditional keyword-based search falls short in capturing the nuanced meaning and contextual relevance of information. This program bridges that gap, empowering professionals to build highly intelligent, context-aware search systems that unlock the true potential of unstructured data, enhancing user experience and driving significant business value.
Participants will gain hands-on experience with cutting-edge tools and frameworks, learning to generate, store, and query high-dimensional vector embeddings for various data types, including text, images, and multimodal content. The curriculum emphasizes practical application, covering Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) algorithms, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architectures, and strategies for performance optimization and scalability. By mastering these advanced concepts, attendees will be able to design and implement robust AI-powered search solutions that significantly improve the accuracy and relevance of information retrieval for next-generation LLM applications.
Course Duration
10 days
Course Objectives
- Understand the fundamental principles of vector embeddings and their role in representing semantic meaning for unstructured data.
- Master the architecture and functionalities of leading vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant, Milvus, Chroma).
- Implement efficient data ingestion and indexing strategies for high-dimensional vectors.
- Apply various embedding models (e.g., BERT, GPT, Sentence Transformers) for diverse data types (text, image, audio).
- Develop robust semantic search pipelines leveraging vector similarity for enhanced information retrieval.
- Optimize Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) algorithms (e.g., HNSW, IVF) for fast and accurate similarity queries.
- Integrate vector databases with Large Language Models (LLMs) for advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
- Design and build AI-powered recommendation systems using vector embeddings.
- Explore multimodal embeddings and their applications in cross-modal search.
- Address challenges related to scalability, latency, and data quality in production-grade vector search systems.
- Evaluate and fine-tune vector database parameters for optimal performance optimization and resource utilization.
- Implement hybrid search techniques combining semantic and keyword-based approaches.
- Gain insights into the future of search and the evolving landscape of generative AI and AI agents.
Organizational Benefits
- Significantly improve the accuracy and relevance of internal and external search capabilities, leading to faster access to critical information and improved decision-making.
- Empower LLMs with up-to-date, relevant contextual data, reducing hallucinations and improving the quality of generated responses through RAG.
- Deliver more personalized recommendations, intuitive chatbots, and intelligent search functions for end-users, boosting satisfaction and engagement.
- Stay ahead of the curve by leveraging cutting-edge AI technologies to build innovative products and services.
- Unlock new insights and value from unstructured data by enabling sophisticated semantic analysis.
- Equip engineering teams with the skills to rapidly prototype and deploy advanced AI search solutions.
- Build resilient and scalable systems capable of handling massive volumes of high-dimensional data.
Target Audience
- AI/ML Engineers
- Data Scientists
- Software Developers.
- Product Managers
- Data Architects.
- Researchers
- DevOps Engineers.
- Anyone interested in Generative AI and LLM optimization.
Course Outline
Module 1: Introduction to Semantic Search & LLM Context
- Understanding the limitations of keyword search in the age of AI.
- The paradigm shift from keyword matching to meaning-based retrieval.
- Role of semantic search in augmenting LLMs and preventing hallucinations.
- Overview of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture.
- Case Study: How a major e-commerce platform boosted product discoverability by 30% using semantic search for customer queries.
Module 2: Fundamentals of Vector Embeddings
- What are vector embeddings? Dense numerical representations of data.
- Techniques for generating embeddings (Word2Vec, GloVe, FastText).
- Understanding embedding spaces and semantic similarity (cosine similarity).
- Evaluating embedding quality and common pitfalls.
- Case Study: Analyzing how news organizations use text embeddings to group similar articles and identify trending topics.
Module 3: Advanced Embedding Models for Diverse Data
- Leveraging Transformer-based models (BERT, Sentence Transformers) for text embeddings.
- Generating image and video embeddings (e.g., CLIP, ResNet features).
- Introduction to multimodal embeddings for cross-modal search.
- Fine-tuning pre-trained embedding models for specific domains.
- Case Study: A media company implementing multimodal search to find relevant video clips based on text descriptions or image content.
Module 4: Introduction to Vector Databases
- Why traditional databases fail for high-dimensional vector data.
- Core concepts of vector databases: indexing, similarity search, CRUD operations.
- Key features and architectural considerations for vector databases.
- Managed vs. open-source vector database options.
- Case Study: A startup choosing a vector database for their personalized content recommendation engine.
Module 5: Deep Dive into Popular Vector Databases (Part 1)
- Pinecone: Architecture, indexing strategies, and basic operations.
- Weaviate: GraphQL API, schema design, and data import.
- Practical hands-on exercises with Pinecone and Weaviate SDKs.
- Performance benchmarks and considerations for each database.
- Case Study: A SaaS company migrating from a custom vector index to Pinecone for scalability.
Module 6: Deep Dive into Popular Vector Databases (Part 2)
- Qdrant: Features, filtering capabilities, and deployment options.
- Milvus: Open-source, distributed architecture, and integration with ML frameworks.
- Chroma: Ease of use for LLM applications and local development.
- Comparative analysis of different vector database strengths and weaknesses.
- Case Study: A financial institution using Qdrant for real-time anomaly detection in transaction data.
Module 7: Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) Algorithms
- The necessity of ANN for high-dimensional similarity search.
- Understanding common ANN algorithms: HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds).
- IVF (Inverted File Index) and other quantization techniques.
- Trade-offs between accuracy, speed, and memory usage in ANN.
- Case Study: Benchmarking different ANN algorithms for a large-scale image recognition system.
Module 8: Building Semantic Search Pipelines
- Data preprocessing and chunking strategies for text.
- Embedding generation and storage in a vector database.
- Designing query embedding generation and similarity search logic.
- Post-processing and ranking of search results.
- Case Study: Building a research paper semantic search engine for academic institutions.
Module 9: Optimizing Similarity Search Performance
- Indexing parameters and their impact on query speed and recall.
- Techniques for dimensionality reduction (e.g., PCA, UMAP).
- Batch processing and parallelization for large-scale queries.
- Monitoring and troubleshooting vector database performance.
- Case Study: Optimizing the search latency for a customer support knowledge base with millions of documents.
Module 10: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Architectures
- Deep dive into the RAG workflow: query embedding, retrieval, LLM generation.
- Integrating vector databases with popular LLM frameworks (LangChain, LlamaIndex).
- Strategies for chunking and context management for RAG.
- Evaluating RAG performance: relevance, coherence, and factuality.
- Case Study: Developing an intelligent chatbot that answers domain-specific questions by retrieving information from a vector database.
Module 11: Advanced RAG Techniques & Use Cases
- Advanced prompt engineering for RAG-powered LLMs.
- Handling complex queries and multi-turn conversations.
- Building conversational AI agents with persistent memory.
- Using RAG for data summarization and content generation.
- Case Study: A legal tech firm using RAG to provide expert insights from legal documents to lawyers.
Module 12: Multimodal Semantic Search & Applications
- Combining text, image, and audio embeddings for unified search experiences.
- Building cross-modal recommendation systems.
- Applications in content moderation and media analysis.
- Challenges and future directions in multimodal AI search.
- Case Study: A social media platform implementing multimodal search to detect inappropriate content across various media types.
Module 13: Scalability and Deployment of Vector Search Systems
- Designing scalable vector database deployments (distributed systems, sharding).
- Containerization (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) for production.
- Cloud-native deployments and managed services.
- Monitoring, logging, and alerting for robust operations.
- Case Study: Scaling a personalized news feed system to millions of users globally.
Module 14: Enterprise Use Cases & Future Trends
- Semantic search in healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
- Vector databases for fraud detection and anomaly detection.
- The role of vector databases in the broader AI ecosystem.
- Emerging trends: graph neural networks, federated learning with embeddings.
- Case Study: A manufacturing company using vector search for defect detection in product images.
Module 15: Best Practices, Ethics & Responsible AI
- Data governance and privacy considerations for embeddings.
- Mitigating bias in embedding models and search results.
- Ethical implications of AI-powered semantic search.
- Continuous learning and model updates in production.
- Case Study: Addressing fairness and bias in a hiring recommendation system powered by semantic matching.
Training Methodology
This course employs a blended learning approach, combining instructor-led live sessions with extensive hands-on labs and interactive exercises. The methodology is designed for technical professionals, focusing on practical application and immediate skill development.
- Interactive Lectures & Discussions: Engaging presentations with Q&A sessions to foster understanding of core concepts.
- Hands-on Coding Labs: Practical exercises using Python, popular vector database SDKs (e.g., pinecone-client, weaviate-client), and LLM frameworks (langchain, llamaindex).
- Real-world Case Studies: In-depth analysis of industry applications to illustrate practical relevance.
- Group Projects & Collaborative Problem Solving: Opportunities to apply learned skills to solve complex challenges in a team environment.
- Live Demos: Demonstrations of setting up and interacting with vector databases and LLM integrations.
- Troubleshooting & Debugging Sessions: Practical guidance on identifying and resolving common issues.
- Self-Paced Learning Resources: Access to code repositories, documentation, and supplementary readings for continued learning.
- Assessment & Feedback: Quizzes, coding challenges, and instructor feedback to gauge comprehension and progress.
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally- recognized certificate.