Training course on Food Safety and Hygiene Management (HACCP Principles)
Training Course on Food Safety and Hygiene Management (HACCP Principles) is meticulously designed to equip aspiring and current food and beverage professionals, executive chefs, kitchen managers, quality assurance specialists, and public health officers with the advanced theoretical insights and practical tools necessary to excel in Food Safety and Hygiene Management (HACCP Principles).
Skills Covered
Course Overview
Training Course on Food Safety and Hygiene Management (HACCP Principles)
Introduction
In the global food service and hospitality industry, ensuring Food Safety and Hygiene is not merely a legal obligation; it is a fundamental ethical imperative and a cornerstone of public health, consumer trust, and business sustainability. A single lapse in food safety can lead to severe public health crises, extensive financial losses, irreparable reputational damage, and devastating legal consequences. Modern food operations demand a systematic and proactive approach to managing potential hazards, which is why the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system has become the internationally recognized standard for ensuring food safety from farm to fork. HACCP provides a preventative, science-based framework for identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards, minimizing risks before they occur. Beyond HACCP, comprehensive hygiene management encompassing personal practices, facility sanitation, and pest control is essential to create a safe and compliant food environment.
Training Course on Food Safety and Hygiene Management (HACCP Principles) is meticulously designed to equip aspiring and current food and beverage professionals, executive chefs, kitchen managers, quality assurance specialists, and public health officers with the advanced theoretical insights and practical tools necessary to excel in Food Safety and Hygiene Management (HACCP Principles). We will delve into the fundamental principles of food microbiology and contamination, master safe food handling practices across the entire food chain, and explore the intricacies of implementing robust sanitation programs. A significant focus will be placed on understanding and applying all seven HACCP principles, from conducting thorough hazard analyses to establishing critical control points, monitoring procedures, and maintaining meticulous records. Furthermore, the course will cover essential aspects of regulatory compliance, conducting effective food safety audits, and managing foodborne illness outbreaks. By integrating international best practices, analyzing real-world food safety incidents, and discussing the nuances of building a strong food safety culture, attendees will develop the strategic acumen to lead safe and compliant food operations, foster unparalleled consumer trust, and contribute meaningfully to the public health and profitability of their establishments.
Course Objectives
Upon completion of this course, participants will be able to:
- Analyze the fundamental principles and strategic importance of Food Safety and Hygiene Management.
- Identify and understand various types of food hazards (biological, chemical, physical, allergenic).
- Master personal hygiene practices and cross-contamination prevention techniques.
- Implement safe food handling procedures from purchasing and receiving to storage.
- Apply safe food handling procedures for preparation, cooking, holding, and cooling.
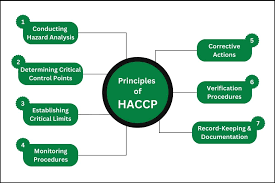
- Conduct a comprehensive Hazard Analysis (Principle 1 of HACCP) for food processes.
- Identify and establish Critical Control Points (CCPs) (Principle 2 of HACCP) in a food operation.
- Define and implement Critical Limits (Principle 3 of HACCP) for each CCP.
- Develop effective Monitoring Procedures (Principle 4 of HACCP) for CCPs.
- Formulate and apply Corrective Actions (Principle 5 of HACCP) when deviations occur.
- Design and execute Verification Procedures (Principle 6 of HACCP) for the HACCP system.
- Establish and maintain meticulous Record-Keeping and Documentation (Principle 7 of HACCP) for food safety.
- Position themselves as leaders in driving food safety compliance and excellence.
Target Audience
This course is designed for professionals across the food and beverage and hospitality sectors who are responsible for food safety:
- Food and Beverage Directors/Managers: Overseeing all F&B operations.
- Executive Chefs and Kitchen Managers: Directly responsible for food production and kitchen hygiene.
- Quality Assurance Managers/Coordinators: Ensuring compliance with food safety standards.
- Restaurant Owners and Operators: Needing to implement and maintain food safety systems.
- Catering Managers: Managing food safety for large-scale events.
- Public Health Inspectors/Professionals: Seeking to understand industry best practices.
- Hotel General Managers: Overseeing overall hotel operations and guest safety.
- Hospitality Students: Specializing in food and beverage management or culinary arts.
Course Duration: 10 Days
Course Modules
Module 1: Introduction to Food Safety and Hygiene
- Importance of Food Safety: Public Health, Economic, Legal, and Reputational Impacts.
- Overview of Foodborne Illnesses: Causes, Symptoms, and High-Risk Populations.
- Key Concepts: Contamination, Spoilage, Shelf Life.
- Legal and Regulatory Landscape of Food Safety (Local and International).
- Building a Culture of Food Safety in the Workplace.
Module 2: Understanding Food Hazards
- Biological Hazards: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi (Sources, Growth Conditions, Prevention).
- Chemical Hazards: Cleaning Agents, Pesticides, Allergens, Heavy Metals (Sources, Prevention).
- Physical Hazards: Glass, Metal, Hair, Jewelry, Plastics (Sources, Prevention).
- Allergen Management: The "Big 8" Allergens, Cross-Contact Prevention, Labeling.
- The Importance of Identifying and Controlling All Hazard Types.
Module 3: Personal Hygiene and Preventing Cross-Contamination
- Handwashing Procedures: Critical Importance and Best Practices.
- Personal Cleanliness: Attire, Hair Restraints, Jewelry, Health Status.
- Preventing Cross-Contamination: Raw vs. Cooked, Equipment, Surfaces, Hands.
- Employee Health and Illness Policies (Exclusion and Restriction).
- Training and Monitoring Staff Hygiene Practices.
Module 4: Safe Food Handling Practices: Purchasing, Receiving, and Storage
- Purchasing: Approved Suppliers, Specifications, Traceability.
- Receiving: Temperature Checks, Visual Inspection, Quality Standards, Documentation.
- Storage: FIFO/FEFO, Temperature Control (Refrigeration, Freezing, Dry Storage).
- Preventing Cross-Contamination in Storage Areas.
- Proper Labeling and Date Marking.
Module 5: Safe Food Handling Practices: Preparation, Cooking, Holding, Cooling, and Reheating
- Preparation: Thawing, Washing, Minimizing Time in Temperature Danger Zone.
- Cooking: Achieving Safe Internal Temperatures (Critical Limits for various foods).
- Hot Holding: Maintaining Safe Temperatures, Equipment Use.
- Cooling: Two-Stage Cooling Method, Rapid Cooling Techniques.
- Reheating: Reheating to Safe Temperatures, Single Reheating Policy.
Module 6: Introduction to HACCP and Principle 1: Conduct a Hazard Analysis
- History and Evolution of HACCP.
- The Seven Principles of HACCP.
- Benefits of Implementing a HACCP System.
- Principle 1: Conduct a Hazard Analysis: Identifying potential biological, chemical, physical hazards.
- Assessing Hazard Significance: Likelihood and Severity.
Module 7: HACCP Principles 2 & 3: Determine CCPs and Establish Critical Limits
- Principle 2: Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs): Identifying points where hazards can be controlled.
- Using the CCP Decision Tree.
- Common CCPs in Food Operations (e.g., cooking, cooling, hot holding).
- Principle 3: Establish Critical Limits: Measurable boundaries for each CCP.
- Setting appropriate critical limits based on scientific data and regulations.
Module 8: HACCP Principles 4 & 5: Establish Monitoring Procedures and Corrective Actions
- Principle 4: Establish Monitoring Procedures: What, How, When, Who for each CCP.
- Continuous vs. Discontinuous Monitoring.
- Calibration of Monitoring Equipment.
- Principle 5: Establish Corrective Actions: What to do when a critical limit is not met.
- Procedures for product disposition, re-establishing control, and preventing recurrence.
Module 9: HACCP Principles 6 & 7: Establish Verification Procedures and Record-Keeping
- Principle 6: Establish Verification Procedures: Ensuring the HACCP system is working effectively.
- Initial Validation, Ongoing Verification, Reassessment.
- Audits, Calibration Checks, Microbiological Testing.
- Principle 7: Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation: Maintaining accurate records.
- Types of Records: Monitoring Logs, Corrective Action Records, Verification Records.
Module 10: Cleaning, Sanitation, and Pest Control
- Developing a Master Cleaning Schedule.
- Understanding Cleaning Agents and Sanitizers: Selection, Use, Storage.
- Cleaning Procedures for Equipment, Utensils, and Facilities.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for Food Establishments.
- Waste Management and Disposal Procedures.
Module 11: Regulatory Compliance and Food Safety Audits
- Navigating Local, National, and International Food Safety Regulations.
- Preparing for and Responding to Health Inspections.
- Conducting Internal Food Safety Audits and Self-Inspections.
- Understanding Third-Party Audits and Certification Schemes.
- Traceability and Recall Procedures.
Module 12: Foodborne Illness Outbreak Management and Continuous Improvement
- Responding to Suspected Foodborne Illness Incidents.
- Investigation Procedures and Collaboration with Health Authorities.
- Crisis Communication during a Food Safety Incident.
- Learning from Food Safety Incidents and Implementing Preventative Measures.
- Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement in Food Safety.
Training Methodology
- Interactive Workshops: Facilitated discussions, group exercises, and problem-solving activities.
- Case Studies: Real-world examples to illustrate successful community-based surveillance practices.
- Role-Playing and Simulations: Practice engaging communities in surveillance activities.
- Expert Presentations: Insights from experienced public health professionals and community leaders.
- Group Projects: Collaborative development of community surveillance plans.
- Action Planning: Development of personalized action plans for implementing community-based surveillance.
- Digital Tools and Resources: Utilization of online platforms for collaboration and learning.
- Peer-to-Peer Learning: Sharing experiences and insights on community engagement.
- Post-Training Support: Access to online forums, mentorship, and continued learning resources.
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally recognized certificate.
Tailor-Made Course
We also offer tailor-made courses based on your needs.
Key Notes
- Participants must be conversant in English.
- Upon completion of training, participants will receive an Authorized Training Certificate.
- The course duration is flexible and can be modified to fit any number of days.