Training Course on Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) Facilitator Skills
Training Course on Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) Facilitator Skills equips individuals with the essential competencies to effectively lead and manage Failure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis sessions.
Course Overview
Training Course on Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) Facilitator Skills
Introduction
This intensive FMECA Facilitator Skills Training program equips individuals with the essential competencies to effectively lead and manage Failure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis sessions. Participants will gain a comprehensive understanding of the FMECA methodology, including failure identification, risk assessment, and criticality analysis, alongside crucial facilitation techniques for driving successful team-based analyses. The course emphasizes practical application through real-world case studies and interactive exercises, ensuring learners can confidently guide cross-functional teams to proactively identify potential failures, evaluate their impact, and implement effective mitigation strategies. Mastering these skills is paramount for organizations aiming to enhance product and process reliability, improve safety, reduce costs, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
The training goes beyond the technical aspects of FMECA, focusing significantly on developing strong facilitation skills. This includes techniques for effective communication, conflict resolution, stakeholder management, and consensus building within diverse teams. Participants will learn how to structure FMECA workshops, encourage active participation, manage discussions, and document findings accurately. By mastering team facilitation, graduates will be able to unlock the collective expertise of their organizations, leading to more robust and comprehensive FMECA outcomes. This ability to effectively guide teams through the FMECA process is a critical differentiator, ensuring the methodology translates into tangible improvements in operational excellence and risk mitigation.
Course Duration
10 days
Course Objectives
- Understand the core principles and methodologies of Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis (FMECA).
- Develop proficiency in identifying potential failure modes across various systems and processes.
- Master techniques for analyzing the effects of failures on system functionality and safety.
- Learn to apply criticality assessment to prioritize failure modes based on risk.
- Gain skills in risk evaluation and mitigation planning using FMECA outputs.
- Develop expertise in facilitating FMECA workshops with cross-functional teams.
- Enhance communication and interpersonal skills for effective team collaboration during FMECA.
- Learn to utilize FMECA software and tools for efficient data analysis and documentation.
- Understand the integration of FMECA with other reliability engineering methodologies.
- Master techniques for documenting and reporting FMECA findings clearly and concisely.
- Learn to apply FMECA in different industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
- Develop strategies for continuous improvement using insights gained from FMECA.
- Understand relevant industry standards and best practices for FMECA implementation.
Organizational Benefits
- Improved Product and Process Reliability: Skilled facilitators lead to more thorough FMECA analyses, identifying potential failures early in the design or process lifecycle, thus enhancing overall reliability.
- Enhanced Safety: Proactive identification and mitigation of failure modes with critical safety implications, led by trained facilitators, contribute to a safer working environment and reduced risk of accidents.
- Reduced Costs: By preventing failures and minimizing downtime, organizations can significantly reduce maintenance costs, warranty claims, and production losses.
- Increased Efficiency: Well-facilitated FMECA sessions streamline the analysis process, leading to quicker identification of critical issues and faster implementation of corrective actions.
- Better Team Collaboration: Training fosters effective communication and collaboration across different departments, as facilitators can bridge knowledge gaps and encourage participation from all stakeholders.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Capabilities: FMECA training equips employees with a structured approach to problem-solving and risk management, leading to a more proactive and analytical organizational culture.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights from comprehensive FMECA studies, guided by skilled facilitators, enable more informed decisions regarding design changes, maintenance strategies, and resource allocation.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Training ensures that FMECA is conducted according to relevant industry standards (e.g., ISO, AS9100), facilitating compliance and reducing regulatory risks.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: More reliable and safer products and processes lead to increased customer confidence and satisfaction.
- Knowledge Retention and Transfer: Training creates internal expertise in FMECA, ensuring knowledge is retained within the organization and can be effectively transferred to new employees.
- Proactive Risk Management: Skilled facilitators enable organizations to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive risk management, anticipating and mitigating potential issues before they occur.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: By embedding FMECA practices through trained facilitators, organizations foster a culture of continuous improvement and a commitment to excellence.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations with robust FMECA capabilities, driven by skilled facilitators, gain a competitive edge through higher quality products, lower costs, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Target Audience
- Reliability Engineers: Professionals responsible for ensuring the reliability and maintainability of products and processes.
- Quality Engineers: Individuals focused on maintaining and improving the quality of products and processes.
- Maintenance Managers: Leaders overseeing maintenance operations and seeking to minimize equipment downtime.
- Process Engineers: Professionals involved in designing, optimizing, and controlling industrial processes.
- Product Development Teams: Engineers and designers responsible for creating new and improved products.
- Safety Managers: Individuals tasked with ensuring a safe working environment and minimizing safety risks.
- Internal Auditors: Professionals responsible for assessing and improving the effectiveness of risk management and control processes.
- Cross-functional Team Leaders: Individuals who lead teams involved in problem-solving and process improvement initiatives.
Course Outline
Module 1: Introduction to FMECA
- Overview of Reliability and Failure Management
- History and Evolution of FMECA Methodology
- Types of FMECA: System, Design, Process
- Benefits and Applications of FMECA Across Industries
- Understanding Key FMECA Terminology
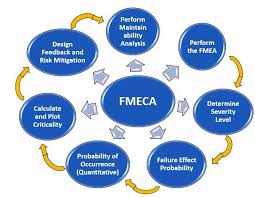
Module 2: The FMECA Process - Step-by-Step
- Defining System Boundaries and Scope
- Identifying Functions and Potential Failure Modes
- Analyzing Failure Effects at Different Levels
- Determining Severity Rankings for Failure Effects
- Identifying Potential Causes of Failure Modes
Module 3: Failure Mode Identification Techniques
- Brainstorming and Team-Based Identification
- Review of Historical Data and Failure Reports
- Utilizing Checklists and Standard Failure Mode Libraries
- Functional Analysis and Block Diagrams
- Interface Analysis and Potential Interactions
Module 4: Failure Effects Analysis
- Understanding Local, Next-Level, and End Effects
- Considering Impact on Safety, Functionality, and Cost
- Documenting Failure Effects Clearly and Concisely
- Using Severity Scales and Ranking Criteria
- Real-World Examples of Failure Effects Analysis
Module 5: Criticality Assessment and Risk Prioritization
- Understanding Probability/Occurrence Rankings
- Calculating Criticality Numbers/Risk Priority Numbers (RPN)
- Developing Risk Matrices and Prioritization Strategies
- Identifying Critical Items and Failure Modes
- Applying Different Criticality Assessment Methods
Module 6: Facilitating FMECA Workshops - The Facilitator's Role
- Essential Skills of an Effective Facilitator
- Planning and Preparing for FMECA Sessions
- Setting Objectives and Ground Rules for Workshops
- Managing Team Dynamics and Participation
- Techniques for Encouraging Open Communication
Module 7: Effective Communication and Interpersonal Skills for Facilitators
- Active Listening and Questioning Techniques
- Managing Conflicts and Disagreements
- Building Consensus and Driving Decisions
- Providing Constructive Feedback to Team Members
- Presenting FMECA Findings to Stakeholders
Module 8: Stakeholder Management in FMECA
- Identifying Key Stakeholders and Their Interests
- Communicating the Value and Purpose of FMECA
- Engaging Stakeholders in the FMECA Process
- Addressing Concerns and Managing Expectations
- Ensuring Buy-in and Support for FMECA Outcomes
Module 9: FMECA Documentation and Reporting
- Developing Standard FMECA Forms and Templates
- Documenting Failure Modes, Effects, and Causes Accurately
- Recording Criticality Assessments and Risk Mitigation Actions
- Creating Clear and Concise FMECA Reports
- Managing and Updating FMECA Documentation
Module 10: Integrating FMECA with Other Reliability Methodologies
- Relationship between FMECA and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
- Using FMECA in conjunction with Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
- Integrating FMECA with Design for Reliability (DFR) Principles
- Applying FMECA within Six Sigma and Lean Initiatives
- Complementary Tools and Techniques for Reliability Analysis
Module 11: Applying FMECA in the Automotive Industry
- Specific Failure Modes and Effects in Automotive Systems
- FMECA Standards and Guidelines in the Automotive Sector (e.g., AIAG)
- Case Studies of FMECA Application in Automotive Design and Manufacturing
- Addressing Safety-Critical Failures in Vehicles
- Utilizing FMECA for Continuous Improvement in Automotive Processes
Module 12: Applying FMECA in the Aerospace Industry
- Unique Challenges and Criticality Considerations in Aerospace
- FMECA Standards and Regulations for Aerospace (e.g., MIL-STD-1629)
- Analyzing Complex Systems and Interdependencies in Aircraft
- Focusing on Safety and Mission-Critical Failures
- Examples of FMECA in Aerospace Design and Maintenance
Module 13: Applying FMECA in the Manufacturing Industry
- Identifying Failure Modes in Manufacturing Processes and Equipment
- Analyzing Impact on Production Efficiency and Quality
- Applying FMECA to Improve Equipment Reliability and Reduce Downtime
- Considering Human Factors and Potential Operator Errors
- Case Studies of FMECA in Various Manufacturing Sectors
Module 14: Advanced FMECA Techniques and Software Tools
- Introduction to FMECA Software Packages
- Utilizing Software for Data Management and Analysis
- Implementing Variations of FMECA (e.g., Functional FMECA)
- Considering Uncertainty and Variability in FMECA
- Future Trends and Advancements in FMECA Methodologies
Module 15: Implementing and Sustaining FMECA within an Organization
- Developing an Organizational FMECA Implementation Plan
- Training and Educating Employees on FMECA Principles
- Establishing Roles and Responsibilities for FMECA Activities
- Integrating FMECA into Existing Business Processes
- Monitoring the Effectiveness of FMECA and Ensuring Continuous Improvement
Training Methodology
This training program utilizes a blended learning approach to maximize engagement and knowledge retention:
- Interactive Lectures: Concise presentations covering the theoretical foundations of FMECA and facilitation skills, incorporating real-world examples and case studies.
- Facilitated Discussions: Guided group discussions to encourage participants to share their experiences, perspectives, and insights related to FMECA and team dynamics.
- Practical Exercises: Hands-on exercises and simulations to apply FMECA principles and practice facilitation techniques in a safe and supportive environment.
- Case Studies: In-depth analysis of real-world FMECA examples from various industries to illustrate best practices and common challenges.
- Role-Playing: Participants engage in role-playing scenarios to practice facilitation skills in different team settings and conflict situations.
- Group Activities: Collaborative tasks that require participants to work together to conduct FMECA analyses and develop risk mitigation strategies.
- Feedback Sessions: Opportunities for participants to receive constructive feedback on their facilitation skills and FMECA application.
- Use of Templates and Tools: Introduction to standard FMECA templates and software tools to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
- Action Planning: Guidance on developing personal action plans to implement learned skills in their respective workplaces.
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally- recognized certificate.
Tailor-Made Course
We also offer tailor-made courses based on your needs.
Key Notes
a.