Phage Display and Library Screening Techniques Training Course
Phage Display and Library Screening Techniques Training Course provides a hands-on, advanced understanding of phage display technology, combinatorial library construction, and high-throughput screening methods for identifying peptides, antibodies, and proteins with high specificity and affinity
Skills Covered
Course Overview
Phage Display and Library Screening Techniques Training Course
Introduction
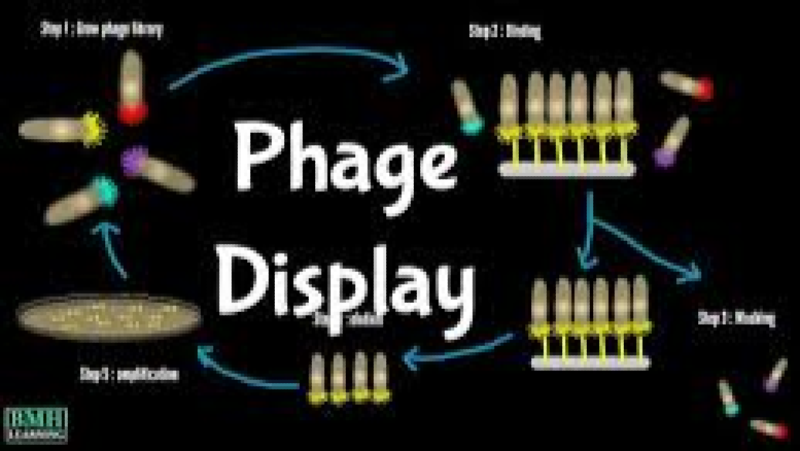
This advanced training course offers an intensive deep dive into Phage Display technology, a Nobel Prize-winning methodology crucial for modern biologics discovery and biotherapeutics development. Participants will gain mastery over the design, construction, and high-throughput screening of combinatorial libraries including antibody phage display (scFv and Fab) and peptide libraries. Phage Display and Library Screening Techniques Training Course is meticulously engineered to bridge theoretical understanding with cutting-edge, practical applications essential for the discovery of novel therapeutic peptides, monoclonal antibodies, and advanced diagnostic agents.
The modern pharmaceutical landscape demands proficiency in techniques that accelerate the hits-to-leads workflow. This course integrates traditional panning and selection methods with Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) analysis and Machine Learning (ML) approaches, ensuring trainees are equipped with the most SEO-friendly and in-demand skills for 2025 and beyond. By focusing on case studies in oncology, infectious diseases, and autoimmunity, we empower scientists to rapidly identify high-affinity binders and translate laboratory discoveries into clinically relevant therapeutic candidates.
Course Duration
10 Days
Course Objectives
- Engineer and construct High-Diversity Combinatorial Libraries (scFv, Fab, and peptide).
- Master the Phage Panning Optimization process for maximized affinity and specificity.
- Design and execute selections against Complex Antigen Targets including membrane proteins and conformational epitopes.
- Utilize Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) data for deep Library Deconvolution and Phage-Seq analysis.
- Apply Bioinformatics Tools for Epitope Mapping and sequence clustering of identified binders.
- Understand and implement Synthetic Antibody Library Design principles for novel biologic scaffolds.
- Troubleshoot and refine M13 Bacteriophage production and titering for optimal yields.
- Isolate and characterize Therapeutic Peptide Leads for targeted drug delivery systems.
- Develop robust screening strategies for Multispecific Antibodies and advanced biologics.
- Integrate Machine Learning (ML) pipelines for predictive selection of high-affinity clones.
- Perform scale-up expression and purification of Recombinant Antibody Fragments in E. coli systems.
- Apply phage display for developing In Vivo Tissue-Targeting and Molecular Imaging agents.
- Navigate the regulatory considerations for transitioning a phage-derived lead into Pre-Clinical Development.
Target Audience
- R&D Scientists in Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Companies.
- Postdoctoral Researchers and PhD Candidates in Molecular Biology, Immunology, or Drug Discovery.
- Lab Managers and Technicians responsible for implementing protein engineering workflows.
- Antibody Engineers seeking to specialize in display platforms.
- Translational Scientists focused on diagnostics and biomarker identification.
- Bioprocess Development personnel interested in upstream protein production.
- Medicinal Chemists transitioning into peptide and biologic drug discovery.
- Bioinformaticians looking to analyze large-scale selection data (Phage-Seq).
Course Modules
Module 1: Phage Display Fundamentals and History
- The central dogma of phage displays and genotype-phenotype linkage.
- Structure and life cycle of the M13 and T7 bacteriophages.
- Comparison of pIII (minor coat) and pVIII (major coat) display systems.
- Understanding monovalent vs. polyvalent display strategies.
- The legacy and Nobel history of the technique.
- Case Study: Analysis of the development timeline for the first fully human antibody derived from phage display (e.g., adalimumab lineage).
Module 2: DNA Library Construction Strategies
- Sourcing genetic material (immune vs. naive libraries).
- Strategies for degenerate and fixed-region PCR amplification.
- Techniques for generating full-length scFv or Fab genes.
- Achieving high transformation efficiency for massive library size.
- Case Study: Designing a synthetic "spiked" library to enrich for humanized scFv frameworks.
Module 3: Antibody Fragment Libraries (scFv and Fab)
- Linking VH and VL domains via flexible peptide linkers.
- Co-expressing light chain and a fusion heavy chain fragment.
- Methods for quantitative assessment of library diversity (titer calculation).
- Assessing library bias and insert verification using sequencing.
- Western blot and ELISA techniques for fragment expression.
- Case Study: Troubleshooting a low-diversity Fab library; identifying failure points in the ligation/transformation step.
Module 4: Peptide and Non-Antibody Libraries
- Design of random oligonucleotides for short peptide display.
- Introducing disulfide bonds or cyclization for stable structures.
- Introducing alternative scaffolds like affibodies or nanobodies.
- Comparing advantages of different display platforms.
- An overview of cell-free selection methods.
- Case Study: Using a cyclic peptide library to screen for high-affinity antagonists of a GPCR.
Module 5: Target Preparation and Immobilization
- Criteria for choosing a biologically relevant target molecule.
- Best practices for purifying recombinant, soluble, or membrane-bound targets.
- Covalent vs. non-covalent immobilization methods (e.g., Biotin-Streptavidin, Ni-NTA).
- Choosing appropriate solid supports (plates, beads, magnetic particles).
- Ensuring the immobilized target remains conformationally active.
- Case Study: Immobilizing a difficult, unstable cell-surface receptor and verifying its integrity for selection.
Module 6: Phage Panning: Selection Strategy (Biopanning)
- Detailed steps: incubation, washing, elution, and amplification.
- Manipulating wash buffer components, pH, and incubation time.
- Strategies to remove non-specific or highly sticky binders.
- Differentiating between closely related or shared epitopes.
- Techniques like acid, base, or competitive elution.
- Case Study: Implementing a multi-round subtractive panning strategy to identify cancer-specific antibodies and discard normal tissue binders.
Module 7: Affinity and Kinetic-Driven Panning
- Designing washes to favor high-affinity, slow-dissociating binders.
- Using soluble antigen or specific ligands for target-specific elution.
- Introduction to label-free techniques (SPR/BLI) used post-panning.
- Strategies for sequential panning rounds and affinity maturation.
- Tailoring chemical or enzymatic elution for specific libraries.
- Case Study: A kinetic panning experiment to isolate antibodies with an off-rate
Module 8: Phage Titering and Recovery
- Optimizing the infection of E. coli cells (e.g., TG1, XL1-Blue).
- Calculating the colony-forming units (CFU) and infectious particles (IFU).
- Large-scale preparation of phage stocks for subsequent rounds.
- Tracking the output/input ratio across panning rounds.
- Long-term storage of phage libraries and stocks.
- Case Study: Calculating the amplification factor of a library between rounds and identifying signs of phage loss or bacterial contamination.
Module 9: Single Clone Identification and ELISA Screening
- Picking individual colonies from the enriched pool.
- Inducing expression of soluble antibody fragments in microplates.
- Screening individual phage clones for binding to the target antigen.
- High-throughput validation of soluble scFv/Fab binding.
- Cross-reactivity screening against irrelevant or related antigens.
- Case Study: Developing a high-throughput sandwich ELISA protocol to identify bispecific scFv clones.
Module 10: Sequence Analysis and Clone Characterization
- Mini-prep and Sanger sequencing of positive clones.
- Sequence Alignment: Identifying unique clones and consensus sequences.
- Using tools to analyze CDR (Complementarity-Determining Region) diversity.
- Using truncated antigens or overlapping peptides to define the binding region.
- Introduction to cloning the fragment into a full-length IgG expression vector.
- Case Study: Using deep sequencing data from a final panning round to identify the top 10 most enriched and unique CDR3 sequences.
Module 11: NGS and Deep Sequencing of Libraries (Phage-Seq)
- The shift from single-clone picking to deep sequencing of entire pools.
- Generating sequencing libraries from the output phage DNA.
- Processing raw sequencing data (FASTQ) to identify unique V-gene reads.
- Calculating fold enrichment and depletion of specific sequences across rounds.
- Generating heatmaps and network plots of highly enriched clones.
- Case Study: Analyzing NGS data from a four-round panning experiment to visually track the convergent selection of dominant clones.
Module 12: Advanced Applications in Therapeutics
- Using phage display to identify linkers or partners for Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) and multi-specific constructs.
- Discovering targets for CAR T-cell or TCR engineering.
- Isolating protective antibodies against bacterial or viral toxins.
- Engineering lytic phages for specific antibacterial applications.
- Phage display for developing novel diagnostic reagents in transfusion medicine.
- Case Study: Engineering a bispecific antibody fragment that simultaneously targets a tumor antigen and a T-cell receptor.
Module 13: Diagnostics and Molecular Imaging
- Screening libraries against serum or cell lysates to find disease-associated targets.
- Generating high-affinity probes for immunohistochemistry (IHC) or flow cytometry.
- Selecting peptides that specifically home to a tissue or tumor site in vivo.
- Conjugating peptides derived from phage display with imaging agents.
- Utilizing phage-derived binders in rapid diagnostic test formats.
- Case Study: Discovering a novel peptide that specifically targets the vasculature of glioblastoma tumors for imaging purposes.
Module 14: Safety, Regulatory, and IP Landscape
- Handling of biological materials, bacteria, and phage stocks.
- Overview of IND-enabling studies for phage-derived leads.
- Key patent families and strategies for protecting novel binders.
- Strategies for reducing immunogenicity and improving stability.
- Pre-Clinical Assays: In vitro functional assays (e.g., cell killing, blocking) before in vivo studies.
- Case Study: Reviewing a patent application for a phage-derived antibody, focusing on the claims protecting the CDR sequences.
Module 15: Automation and Machine Learning Integration
- Implementing robotic systems for liquid handling in panning.
- Utilizing microfluidic chips for ultra-low volume selections.
- Using algorithms to design in silico optimized synthetic libraries.
- Training models to predict binding affinity based on sequence data.
- Combining phage display with single-cell sequencing and spatial proteomics.
- Case Study: A simulation exercise where a Machine Learning model flags potential high-affinity clones from a Phage-Seq dataset, which the trainee then prioritizes for validation.
Training Methodology
- Interactive Lectures.
- Hands-on/Virtual Lab Simulations
- In-Depth Case Studies
- Bioinformatics Workshops.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving.
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally- recognized certificate.
Tailor-Made Course
We also offer tailor-made courses based on your needs.
Key Notes
a. The participant must be conversant with English.
b. Upon completion of training the participant will be issued with an Authorized Training Certificate
c. Course duration is flexible and the contents can be modified to fit any number of days.
d. The course fee includes facilitation training materials, 2 coffee breaks, buffet lunch and A Certificate upon successful completion of Training.
e. One-year post-training support Consultation and Coaching provided after the course.
f. Payment should be done at least a week before commence of the training, to DATASTAT CONSULTANCY LTD account, as indicated in the invoice so as to enable us prepare better for you.